Why does your ankle hurt?
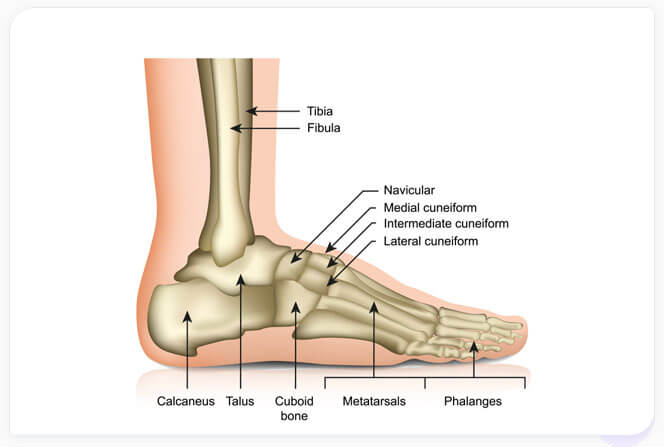
The ankle joint connects your leg bones to your foot. It is required in order to move your foot up, down, inwards, and outwards (See Figure 1).
The bones in the joint are covered in a slippery cartilage that absorbs shock and reduces friction so that the bones move smoothly. Tendons connect various muscles to the bones and ligaments connect bones to each other.
Together these components allow the ankle to absorb forces several times greater than your body weight. Damage or injury can severely limit mobility and cause significant pain.
Regenerative Medicine can help alleviate ankle joint injuries without using steroids or resorting to surgery.
Figure 1: Bones composing the ankle and foot. The ankle joint is composed of the two leg bones, the tibia and fibula, that form the inside and outside of the ankle, respectively. They meet the foot at the talus, a small bone just above the heel or calcaneus.Causes, Signs And Symptoms of Foot Pain
Because the ankle is comprised of bones and soft tissues there are many possible reasons for ankle pain.
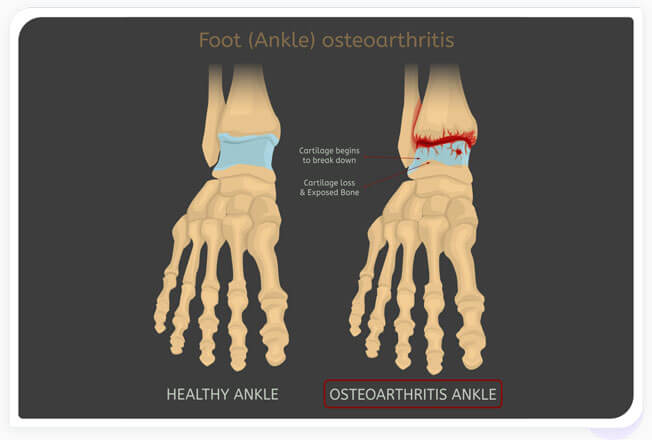
Common causes of ankle pain include:- Osteoarthritis: ankle arthritis involves the breakdown of cartilage in the ankle joint due to wear and tear, or repetitive, overuse (see Figure 2 below).
- Sprains, strains, tears: Overstretched ligaments, partially torn or torn ligaments are very common injuries
- Fractures: bones fractures involving the tibia can cause outside ankle pain. A fractured fibula can cause inside ankle pain.
- Bone spurs: Osteophytes or bony growths can form on the bones in the heel and toes resulting in ankle pain as you compensate.
- Ankle Tendonitis: Involves the inflammation of any of the tendons in the foot (see below)
- Bursitis: Ankle bursitis occurs when the bursa, a small fluid filled sac at the back of the foot between the Achilles tendon and heel, becomes inflamed.
- Infection
- Rheumatoid arthritis: An autoimmune disease that attacks the joints.
- Gout: A buildup of uric acid crystals in the joint
- Figure 2. Ankle osteoarthritis is depicted on the right where the articular cartilage covering the ends of the leg bones where they join the foot at the talus has cracked and degraded. Friction buildup can cause stiffness, pain, and immobility.

Symptoms of ankle pain vary according to the location of the injury (top, side, or bottom of the foot) and the cause.
Symptoms of ankle osteoarthritis include:- Crepitus: crunching, popping, or grating noises coming from the ankle joint
- Dull aching pain that may be worse in the morning or after inactivity
- Joint stiffness
- Ankle swelling and pain
- Decreased mobility: decreased range of motion limits flexibility
- Pain from bone spurs that accompany tendonitis, may lead to ankle impingement
- Pain following the length of the tendon
- Pain at the attachment point of the tendon to the bone
- Tendon stiffness or sore ankle when waking up in the morning or after inactivity
- Back of ankle pain (Achilles tendonitis, peroneal tendonitis), inner ankle pain (tibial tendonitis), pain stretching toes (flexor tendonitis), pain across top of foot (extensor tendonitis)
- Age. Changes in the cells and extracellular matrix of joint tissues that occur in aging increase the susceptibility of older adults to OA, in addition to more wear and tear over time.
- Sex. Women are more likely to develop osteoarthritis, this may be related to age-related nutritional deficiencies and hormonal changes (e.g., menopause).
- Obesity. Being overweight places excess burden on the body's joints and may increase the pace of cartilage degeneration as does a sedentary lifestyle.
- Repeated stress on the joint. Repetitive activities can damage tendons and ligaments and lead to more wear and tear in joints. This can involve activities related to one's profession or sporting activities.
- Previous trauma. Trauma to ligaments and tendons in the ankle or to the bones increase the risk for OA.
- Genetics. There is a higher risk of developing OA if it runs in the family.
- Bone deformities. Abnormal bone structure increases the stress at joint, muscles, tendons, ligaments contributing to OA, tendonitis, and bursitis.
- Metabolic diseases. Changes in the mineral content and health of the tissues and bones in the foot that can lead to increased risk for OA.

Our specialists diagnosis foot pain by using a multipronged approach:
- Medical History: Our doctors will ask you about the nature of your ankle pain (e.g., when and under what conditions you experience ankle and foot pain). They will ask about prior surgeries, accidents, and trauma to the foot, ankle, and leg.
- Physical Exam: The doctor will examine the range of motion of the ankle, look for swelling and muscle/tendon tightness.
- Imaging with X-Rays or MRI: X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRIs) are used to determine if your ankle pain is due to arthritis, fractures, or damage to tendons and ligaments.
Treatment Options
The StemX clinic offers a range of customized Regenerative Medicine for ankle pain.
The StemX Approach
StemX is California's leading provider of holistic and regenerative medicine services. Our experts don't just offer popular treatments, but customized medical solutions based on individual needs.
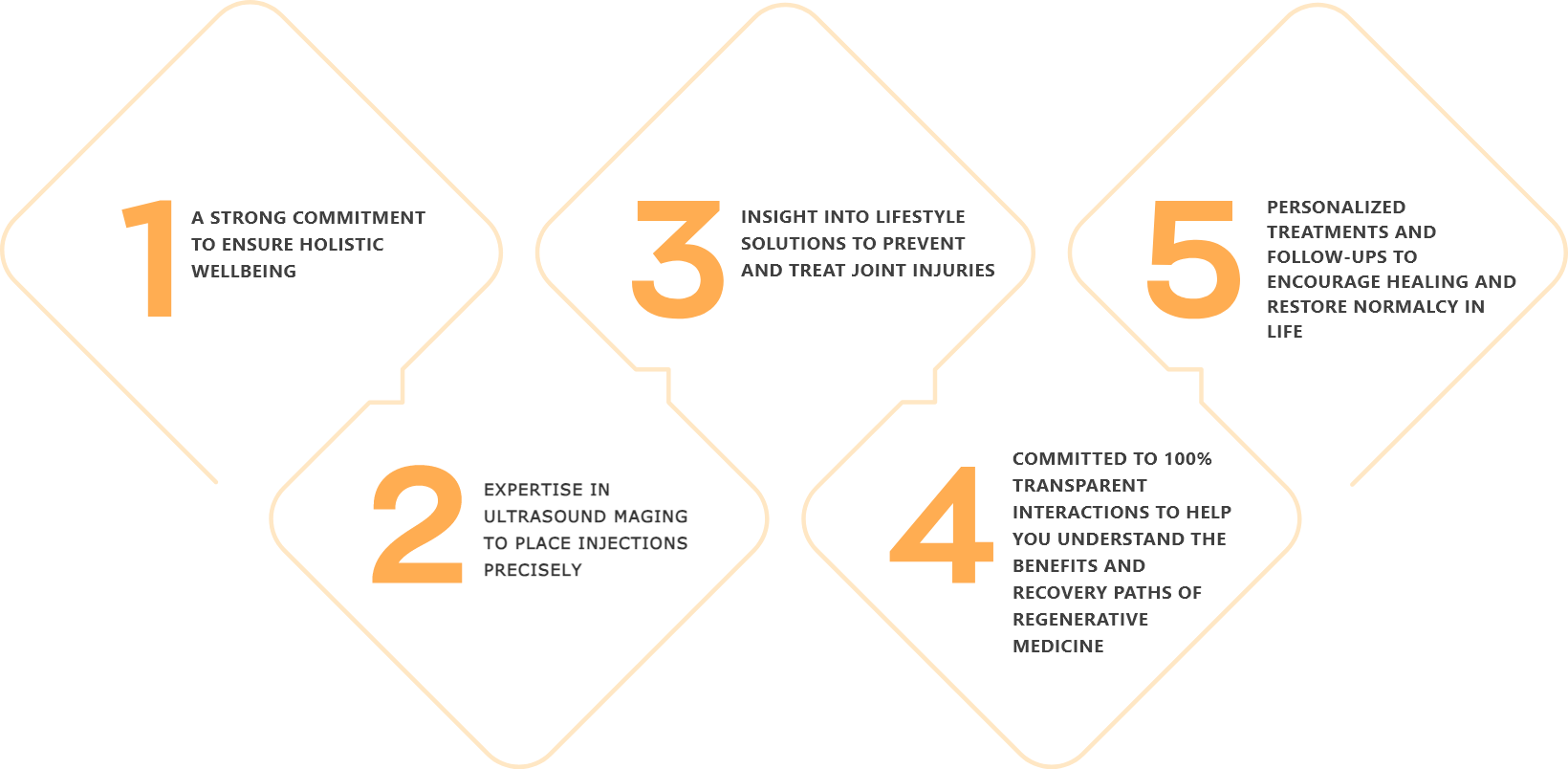
Located in Solana Beach, California, the StemX clinic is composed of a team of expert doctors with years of experience administering regenerative medicine treatments for joint disease. Our team has:





How To Get Started
Treatment Procedure
While each treatment may be customized, you can expect your experience to be similar to the following:
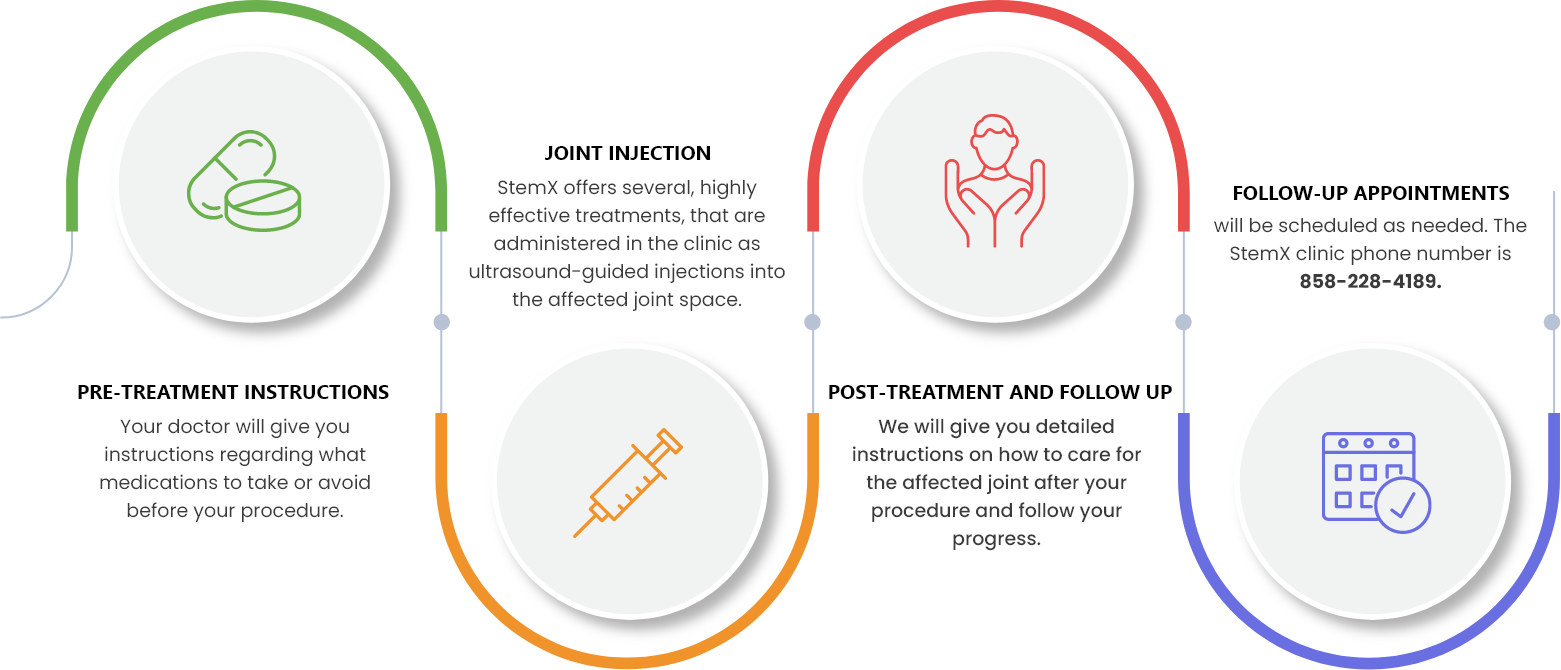




All procedures are conducted in our Solana Beach, California clinic. 124 Lomas Santa Fe Dr #206, Solana Beach, CA 92075.
Frequently Asked Questions
Depending on the severity of ankle pain, it can be treated by resting, icing, stretching, with NSAIDs, regenerative medicine, steroids, or surgery.
Ankle pain is most often a symptom of arthritis or injuries to tendons and ligaments in the joint area.
The time to heal ankle pain depends on the nature and severity of the injury. A doctor should be consulted for serious ankle pain.
Arthritis in the ankle can be dull and achy or sore due to inactivity. Crepitus or locking of the joint may also be present.
Regenerative medicine approaches can help repair damaged cartilage in the ankle and reduce inflammation in surrounding tissues.
Arthritis cannot be completely cured because it is due to wear and tear. It can be treated and controlled, however.
Ankle arthritis can occur in ~1% of people. While not as common as knee arthritis it still occurs especially after injuries.
Physical therapy to strengthen the legs and muscles near the ankle is very helpful in reducing ankle swelling and pain.
Stage IV osteoarthritis is described as near complete wearing away of articular cartilage and loss of joint space (bone on bone conditions).
Severe arthritis can only be removed if the joint is replaced surgically.
Advanced Regenerative medicine treatments treatments take full effect after a few months. Additional treatments may improve results.
Ankle arthritis can cause serious pain, loss of mobility and cause problems in other joints like the knee and hip due to compensation in the way one walks to avoid pain.
Ankle arthritis progresses according to how much cartilage is damages, the formation of bone spurs, and the loss of joint space.
Regenerative medicine treatments are long lasting, but osteoarthritis is a progressive degenerative disease. Continued wear and tear can cause new damage.



