What is Foot Pain?
Damage to the bones, joints, ligaments, or tendons in the foot can cause significant pain. Most foot pain is the result of either trauma, overuse, or inflammatory conditions.
Causes, Signs And Symptoms of Foot Pain
What are the causes of foot pain?
One common cause of foot pain is osteoarthritis (OA). OA involves the progressive breakdown of articular cartilage that permits bones to slide past each other at joints (see Figure 1).
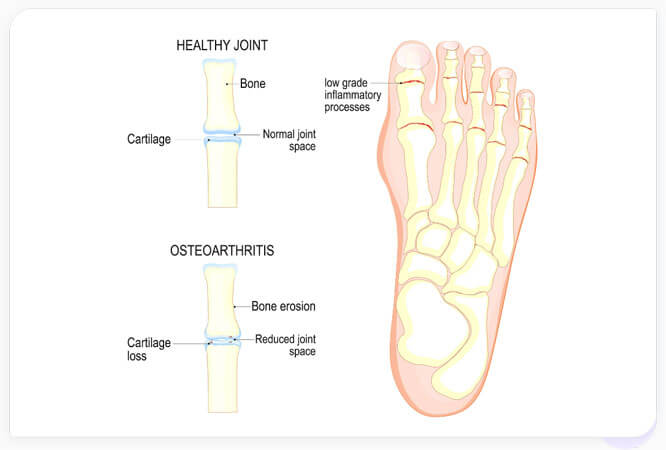
Figure 1: Depiction of foot osteoarthritis. Healthy joints have intact articular cartilage and space between opposing bones in a joint. Arthritic joints have damaged cartilage on each bone that increases the friction between due to decreased joint space.
Other types of foot pain include:- Pain on top of the foot: caused by tight-fitting shoes, or overuse of tendons along the top of the foot pulling the foot upwards.
- Bone spurs: Osteophytes or bony growths can form on the bones in the heel and toes.
- Foot tendonitis: Inflammation of any of the tendons in the foot can cause foot pain (e.g., Achilles tendonitis, extensor tendonitis, peroneal tendonitis, posterior tibial tendonitis, plantar fasciitis)
Symptoms of foot pain vary in location (top, side, or bottom of the foot) and according to the cause.
Symptoms of foot osteoarthritis include:- Crepitus: crunching, popping, or grating noises coming from the joints in the feet
- Pain: dull aching pain especially after activity or wearing uncomfortable shoes
- Joint stiffness
- Joint swelling
- Decreased mobility
- Pain in the first joint that connects the big toe to the foot or in the midfoot
- Pain from bone spurs
- Pain following the length of the tendon
- Pain at the attachment point of the tendon to the bone
- Tendon stiffness when waking up in the morning or after inactivity
- Heel pain

- Age. Changes in the cells and extracellular matrix of joint tissues that occur in aging increase the susceptibility of older adults to OA, in addition to more wear and tear over time.
- Sex. Women are more likely to develop osteoarthritis, this may be related to age-related nutritional deficiencies and hormonal changes (e.g., menopause).
- Obesity. Being overweight places excess burden on the body's joints and may increase the pace of cartilage degeneration as does a sedentary lifestyle.
- Repeated stress on the joint. Repetitive activities can damage tendons and ligaments and lead to more wear and tear in joints. This can involve activities related to one's profession or sporting activities.
- Previous trauma. Trauma to ligaments and tendons in the ankle or to the bones increase the risk for OA.
- Genetics. There is a higher risk of developing OA if it runs in the family.
- Bone deformities. Abnormal bone structure increases the stress at joint, muscles, tendons, ligaments contributing to OA, tendonitis, and bursitis.
- Metabolic diseases. Changes in the mineral content and health of the tissues and bones in the foot that can lead to increased risk for OA.

Our specialists diagnosis foot pain by using a multipronged approach:
- Medical History: Our doctors will ask you about the nature of your foot pain (e.g., when and under what conditions you experience foot pain). They will ask about prior surgeries, accidents, and trauma to the foot, ankle, and leg.
- Physical Exam: The doctor will examine the range of motion of the foot, look for swelling and muscle/tendon tightness.
- Imaging with X-Rays or MRI: X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRIs) are used to determine if your foot pain is due to arthritis, fractures, heel spurs, loss of fatty pad tissue under the heel, or damage to tendons and ligaments.
Treatment Options
The StemX clinic offers a range of customized Regenerative Medicine solutions for foot pain
The StemX Approach
StemX is California's leading provider of holistic and regenerative medicine services. Our experts don't just offer popular treatments, but customized medical solutions based on individual needs.
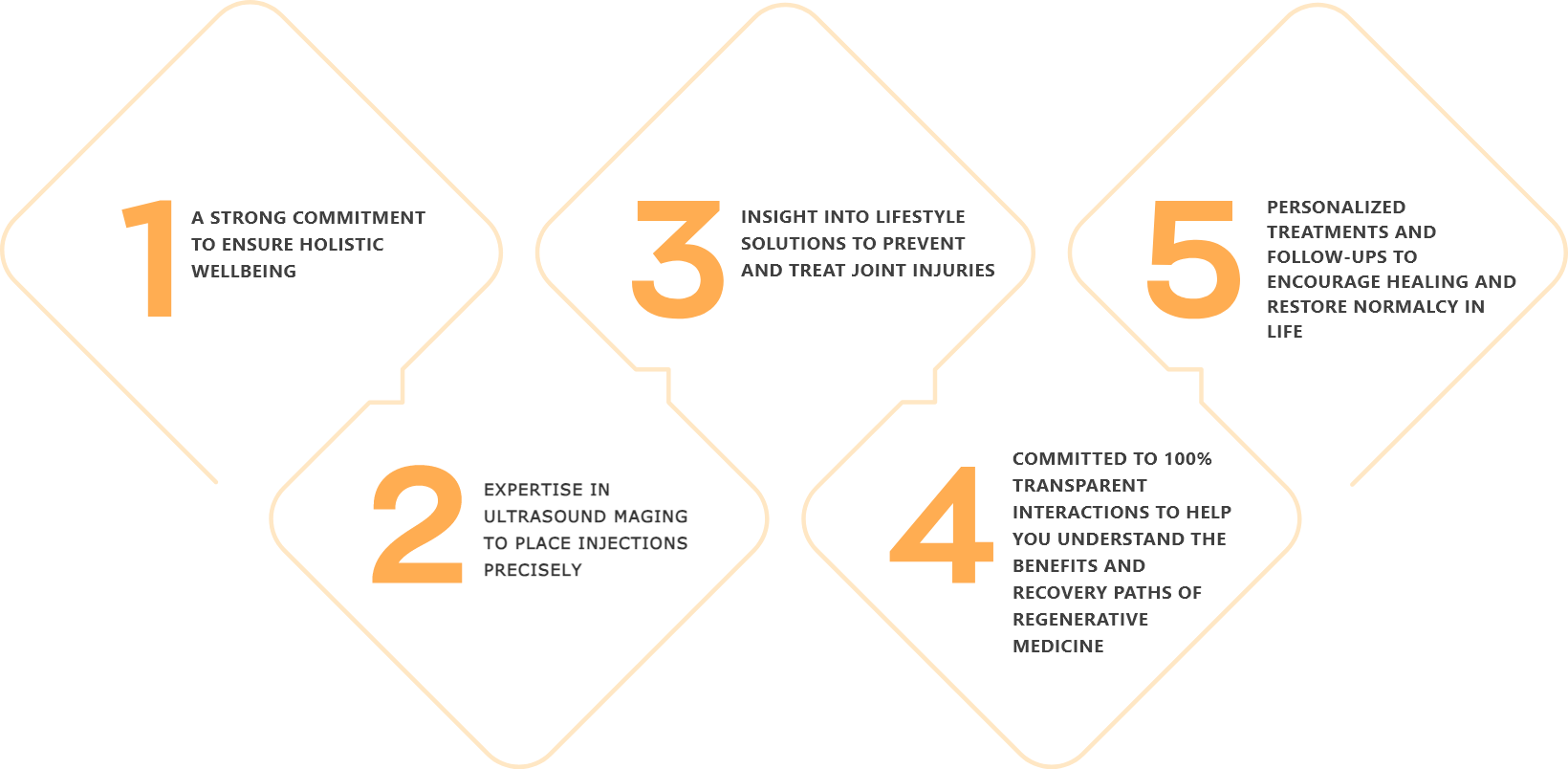
Located in Solana Beach, California, the StemX clinic is composed of a team of expert doctors with years of experience administering regenerative medicine treatments for joint disease. Our team has:





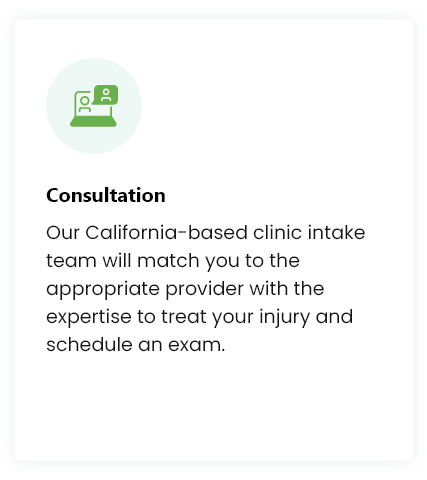
How To Get Started
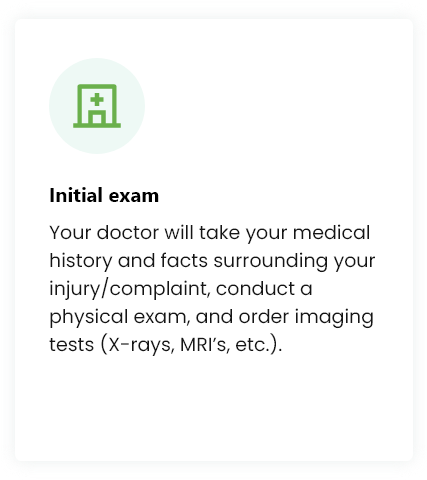
Treatment Procedure
While each treatment may be customized, you can expect your experience to be similar to the following:
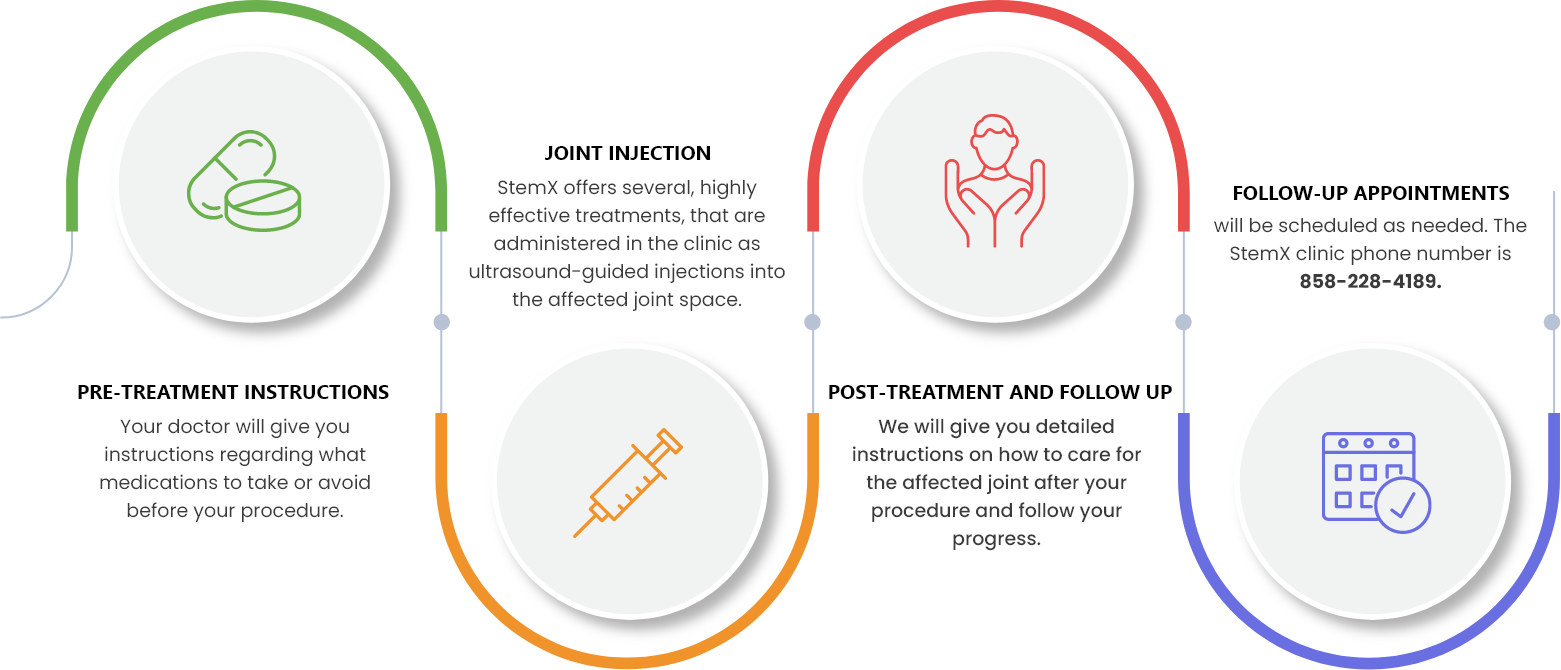




All procedures are conducted in our Solana Beach, California clinic. 124 Lomas Santa Fe Dr #206, Solana Beach, CA 92075.
Frequently Asked Questions
Osteoarthritis and different forms of tendonitis or tendon ruptures are common causes of foot pain. Fractures, broken toes, callouses, corns and bunions also result in foot pain.
Limited mobility, severe pain, or pain or swelling that does not resolve in a few weeks is a sign of serious injury to your foot.
Arthritis, gout, and diabetes are common foot conditions associated with age.
Foot arthritis may be experienced as bottom of foot pain, pain on the side of foot, big toe pain, or pain in middle of foot. Joint stiffness and swelling during rest is also typical.
If foot pain due to exertion doesn't resolve after resting, you may need to talk to your doctor.
Regenerative medicine is well-suited to treat arthritis in feet, big toe joint pain and other joints affected by damaged cartilage. They work to stimulate the body to heal itself with no side effects.
Achy, stiff, and swollen joints are signs of foot arthritis. Your doctor can take X-rays of the foot to confirm a diagnosis.
Regenerative medicine can treat arthritic joints in the foot. Wear and tear cannot be stopped so arthritis can be controlled but not cured.
Modifying activity levels, losing weight, physical therapy, orthotics and treatments including regenerative medicine therapies can prevent foot pain from getting worse.
Improvements in foot arthritis pain can be seen over several weeks to months when receiving regenerative medicine treatments depending on the severity of arthritic disease.
Foot arthritis can limit mobility and cause significant pain if not treated.
Cartilage in affected joints is progressively damaged over time due to wear and tear. Once cartilage is worn away (bone on bone) surgery may be the only way to alleviate pain.
Regenerative medicine treatments are long lasting, but osteoarthritis is a progressive degenerative disease. Continued wear and tear can cause new damage.



