What is tennis elbow?
Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a musculoskeletal condition that causes tendonitis affecting the common extensor tendon that connects forearm muscles to bones in the lateral elbow and wrist (See Figure 1).
The extensor tendons permit the wrist to extend backward away from the palm.
Tendons are a type of connective tissue made up primarily of strong collagenous fibers. However, they are not designed to stretch and extend. This makes the tendons that attach to the medial and lateral epicondyles of the humerus vulnerable to injury.
Elbow tendinopathy represents an important set of pathologies that account for lost recreation time, decreased quality of life, and work-related disability claims.
Figure 1. Tennis elbow or lateral epicondylitis involves pain and inflammation originating from the common extensor tendon on the lateral (outside) elbow at the lateral epicondyle of the humerus (upper arm bone). Micro-tears degrade the tendon in the area shown in red.
Causes, Signs And Symptoms
Lateral elbow pain (or lateral epicondyle pain) usually starts as tenderness in the dominant arm due to repeated overloading of forearm muscles.
Most patients who develop tennis elbow experience some or all of these symptoms:- Stiffness in the forearm causing difficulty in making a fist
- A tender spot on the outside of the elbow
- Pain radiating from your elbow to your forearm and wrist
- Reduction in grip strength
- Tingling and numbness in the affected hand

Tennis elbow is caused by tiny micro-tears in the medial common flexor tendon that connects your elbow to the wrist and finger muscles.
Recurrent tears lead to tendonitis, tissue death, and thickening of the tendon which can cause significant pain.
Specific causes and risk factors for tennis elbow include:- Repeated movements, like arm bending, swinging, flexing, gripping, and twisting of the wrist can cause pain in the lateral elbow.
- Incorrect use of a sports racquet or poor throwing technique while playing rugby, basketball, or baseball
- Occupational hazards for plumbers, carpenters, butchers, painters, computer-mouse users, and builders
- Injuries during weight training due to lack of warmup and conditioning
- It can affect anyone in the 45-64 age bracket, but women are at higher risk than men.
Our Specialists diagnose tennis elbow using a multipronged approach.
- Medical History: Our doctors will ask you about the nature of your elbow, wrist, and finger pain. They will ask about prior surgeries, accidents, and trauma to the arm.
- Physical Exam: The doctor may ask you to move your arm in various ways and against resistance to locate the source of pain to make an affirmative diagnosis.
- Imaging with X-Rays or MRI: X-rays may be used to rule out other causes of your arm/elbow pain. Rarely, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is needed to confirm the diagnosis.

Treatment Options
The StemX clinic offers a range of customized Regenerative Medicine solutions for Tennis Elbow treatment
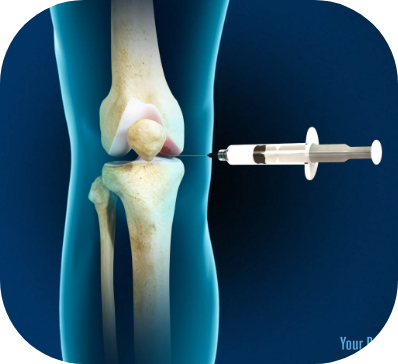
The StemX Approach
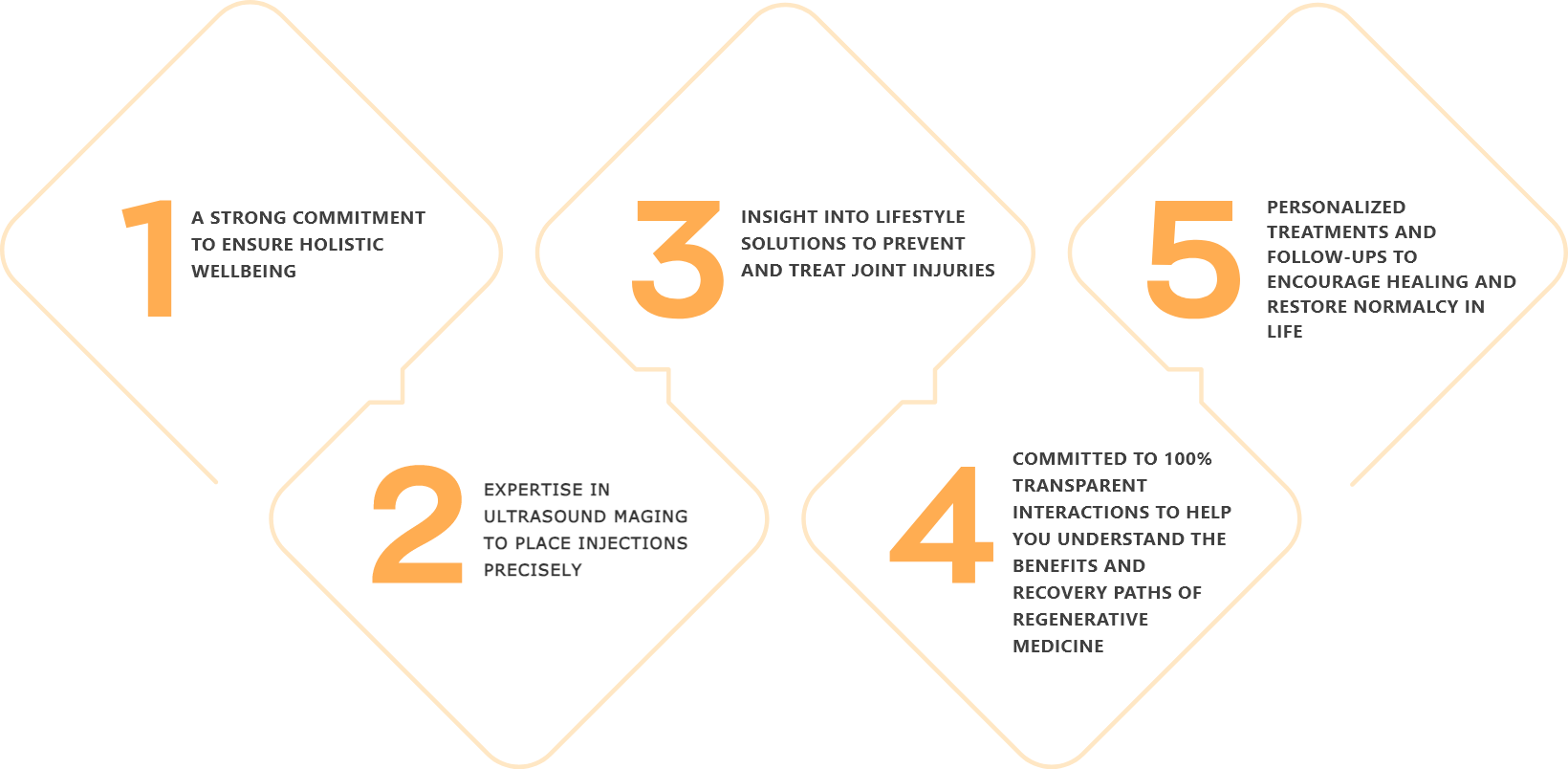
StemX is California's leading provider of holistic and regenerative medicine services. Our experts don't just offer popular treatments, but customized medical solutions based on individual needs.
Located in Solana Beach, California, the StemX clinic is composed of a team of expert doctors with years of experience administering regenerative medicine treatments for joint disease. Our team has:





How To Get Started
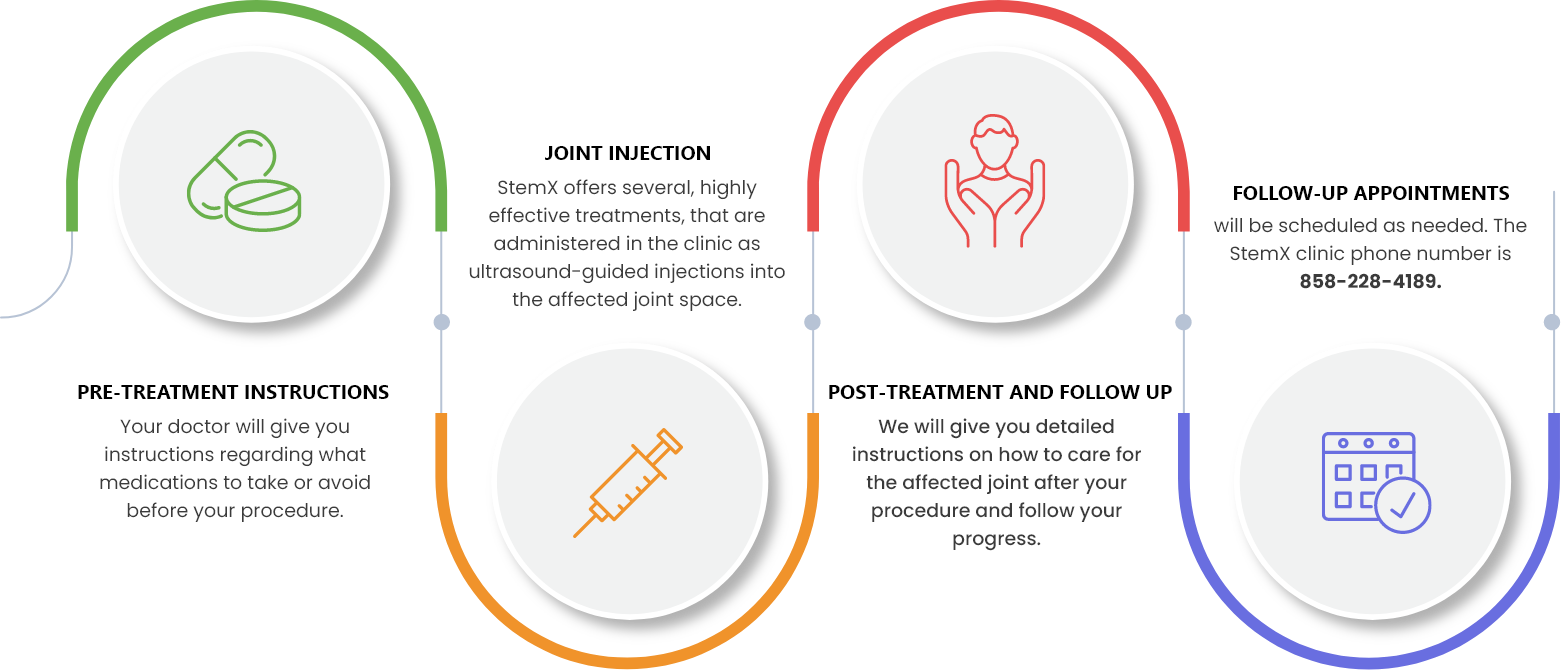
Treatment Procedure
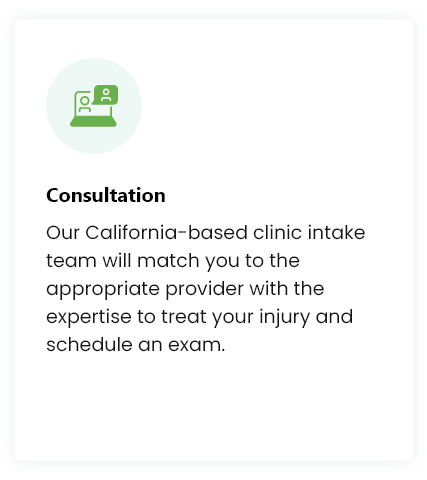
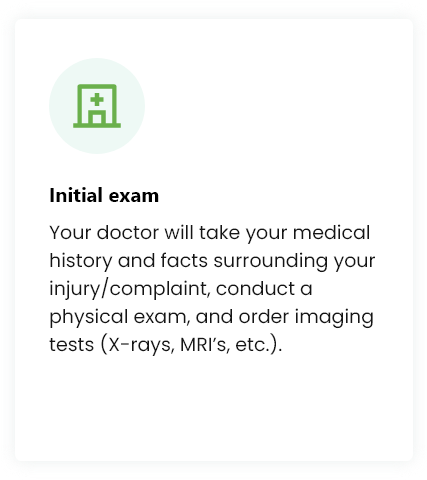
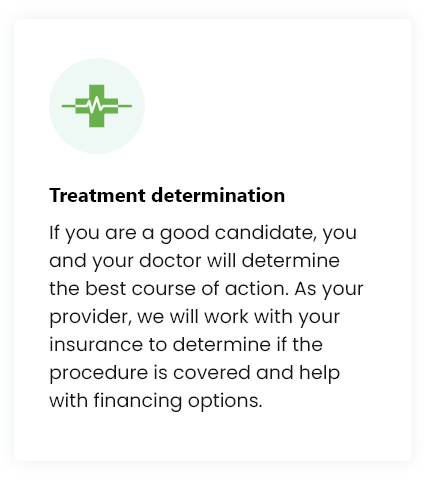
While each treatment may be customized, you can expect your experience to be similar to the following:




All procedures are conducted in our Solana Beach, California clinic. 124 Lomas Santa Fe Dr #206, Solana Beach, CA 92075.
Frequently Asked Questions
A lateral epicondylitis brace, tape or OTC pain relievers along with rest and physical therapy treatment can be used for minor cases. Regenerative medicine is an alternative to steroids/surgery.
Tennis elbow can take 6mo-2yr to heal on its own. With regenerative medicine treatment healing begins in weeks with optimal results after several months.
Minor cases of tennis elbow can take 6mo-2yr to heal on its own. Moderate to serious cases require regenerative medicine treatment or possibly surgery if left untreated.
The extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB), supinator, extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor digitorum, extensor digiti minimi and extensor carpi ulnaris muscle can all be affected.
Regenerative medicine can reduce pain and inflammation in tendons and muscles in the elbow due to tennis elbow and other tendinopathies.
Yes, tennis elbow can be experienced a pain, numbness, and tingling sensations in the fingers.
Severe tendonitis around the elbow, fractures, or dislocated joints could prevent straightening of the arm at the elbow.
Tennis elbow is typically not a serious condition especially if treated properly. In addition to pain, wrist and arm function can be lost if untreated.
Pain gradually develops over time. Swelling is usually present early stages but usually subsides as degeneration of the tendon increases. Lastly, functionality is lost.
No, tennis elbow involves inflammation on the outer (lateral) end of the elbow where golfer's elbow refers to inflammation on the inner (medial) side of the elbow.
Regenerative medicine treatments are long-lasting. Together with tennis elbow physical therapy and rest, further damage can be avoided.
Regenerative Medicine injections cause minimal discomfort. The injection site may be sore for several days during which time strenuous activity is discouraged.
The cost of regenerative medicine treatments vary according to the type of treatment and number of treatments needed which depends on the severity of the injury.



