What Is A Torn Meniscus?
A torn meniscus is one of the most common injuries to the knee involving the thick cup-like cartilage that cushions and supports the femur (upper leg/thigh bone) and tibia (shin) bones in the knee.
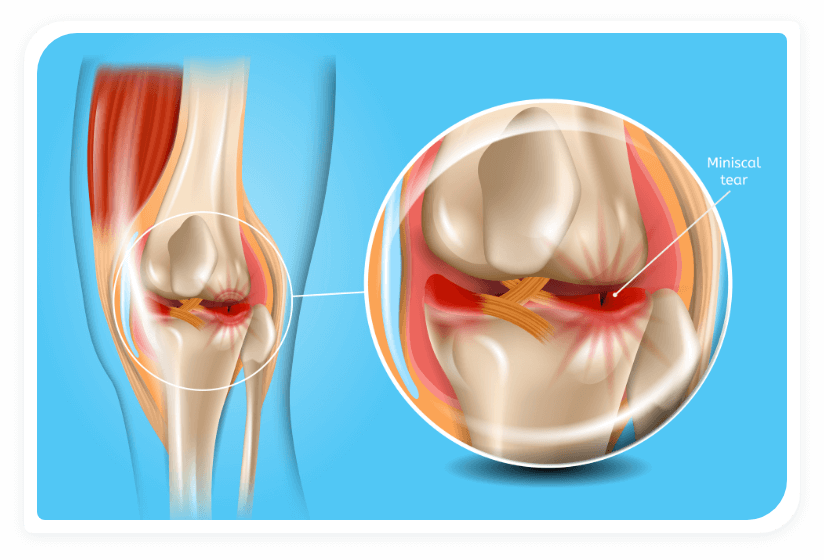
The meniscus is an essential component of the knee joint and without its proper functioning, the knee can become unstable. The menisci are composed of two C-shaped structures divided into medial and lateral components. They are a tough, rubbery form of cartilage that act as shock absorbers (See Figure 1).
The menisci sit between the articular cartilage surfaces providing lubrication and nutrition to the cartilage. They are also responsible for shock absorption, weight distribution, and joint stability.
Menisci in the knee can be torn due to an acute trauma or through a degenerative process associated with aging. The mechanism of injury resulting in acute trauma (tears) to the meniscus is typically a suddenly twisting motion of the knee while bearing weight on it.
Figure 1. Depiction of the right knee joint. Note the lateral and medical meniscal cartilage located between the femur (thighbone) and tibia (shin bone) which form the knee joint.
What are the different kinds of meniscus tears?There are six different types of meniscal tears that vary by the location and severity of the tear (See Figure 2).
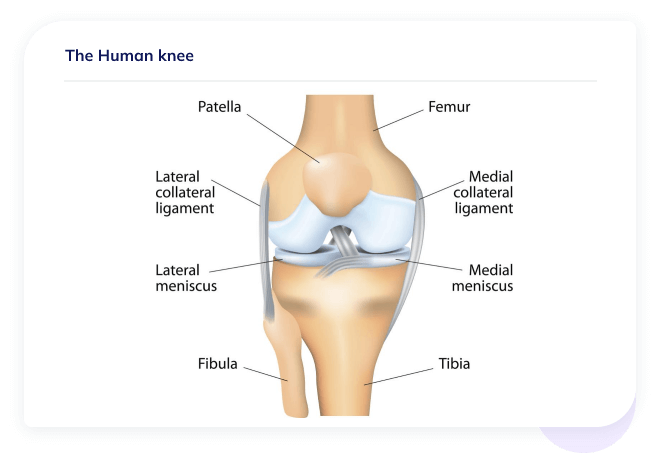
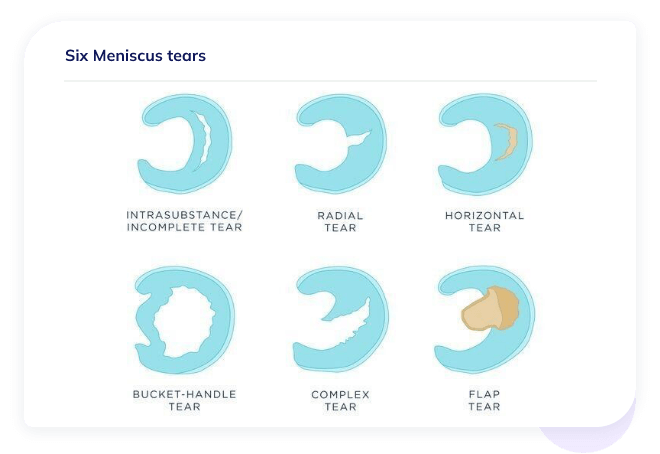
Figure 2. Note to position and severity of the various types of meniscus tears. Untreated meniscal tears can increase risk for osteoarthritis, another debilitating disease involving the breakdown of articular cartilage
- Incomplete/Intrasubstance tears are indicative that the meniscus tissue is undergoing degenerative changes. These injuries are stable and do not require surgery. Regenerative medicine approaches represent a non surgical treatment for torn meniscus of this type.
- Radial tears occur in the area of the knee that is a vascular (isn't supplied with blood) so it cannot heal on its own. Thus, surgery may be required if the tear is severe.
- Horizontal tears can be treated non-surgically with Regenerative Medicine approaches since much of the meniscus is vascularized in this area.
- Bucket Handle tears are similar to horizontal tears but involve a larger portion of the meniscus. A combination of Regenerative Medicine and surgery to restore range of motion to the knee may be the ideal treatment.
- Complex tears are indicative of a mixture of tears and are usually not treated surgically. Regenerative medicine approaches to treat the torn meniscus may provide the best chance to for healing.
- Flap tears may cause a catching sensation in the knee due to the flap of tissue. This can be removed surgically. Regenerative medicine can aid in the healing post operatively.
Causes, Signs And Symptoms
The meniscus in the knee can tear when the knee is violently or forcefully twisted while bearing weight. This is often the case for athletes. However, deep squatting or heavy lifting can also lead to a tear.
What are the symptoms of knee meniscus tears?Upon tearing the meniscus, most people can still walk on their injured knee and many athletes are able to keep playing with a tear. However, the knee will become stiffer and more swollen. The most common symptoms of a meniscus tear are:
- Pain increasing with severity of the tear, can dissipate but return with overuse
- Stiffness and swelling
- Catching, popping, or locking of the knee (especially with severe tears)
- The sensation of instability in the knee, "giving way" or feeling "wobbly"
- Inability to move the knee through its full range of motion
Intense activity (sports) and age seem to increase the likelihood of a meniscus tear but there are other factors as well:
- Age. Those 55-60 years and older are at increased risk of tears due to wear and tear.
- Sex. Males are at increased risk because they participate in risky activities at higher rates.
- Weight. Obesity or being overweight
- Occupation. Work-related kneeling, squatting, and climbing stairs
- Sports. Certain sports like soccer, rugby, football, tennis, and basketball that involve landing on the knee or making sudden pivoting turns Comorbid joint injuries. Not repairing injuries to ligaments in the knee increase the risk of meniscal tears
Our specialists diagnose a torn meniscus using a multipronged approach:
- Medical History: Our doctors will ask you about the nature of your knee pain (e.g., when and under what conditions you experience knee pain). They will ask about prior surgeries, accidents, and trauma to the knee.
- Physical Exam: The doctor will assess your knee function by testing the range of motion, pain when kneeing, listen for any cracking or popping noises (crepitus).
- Imaging with X-Rays or MRI: X-rays can rule out other knee problems but a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan may be needed to detect any tears.
Treatment Options
The StemX clinic offers a range of customized Regenerative Medicine treatments to treat orthopedic injuries.
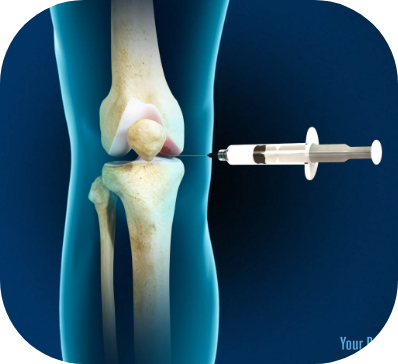
The StemX Approach
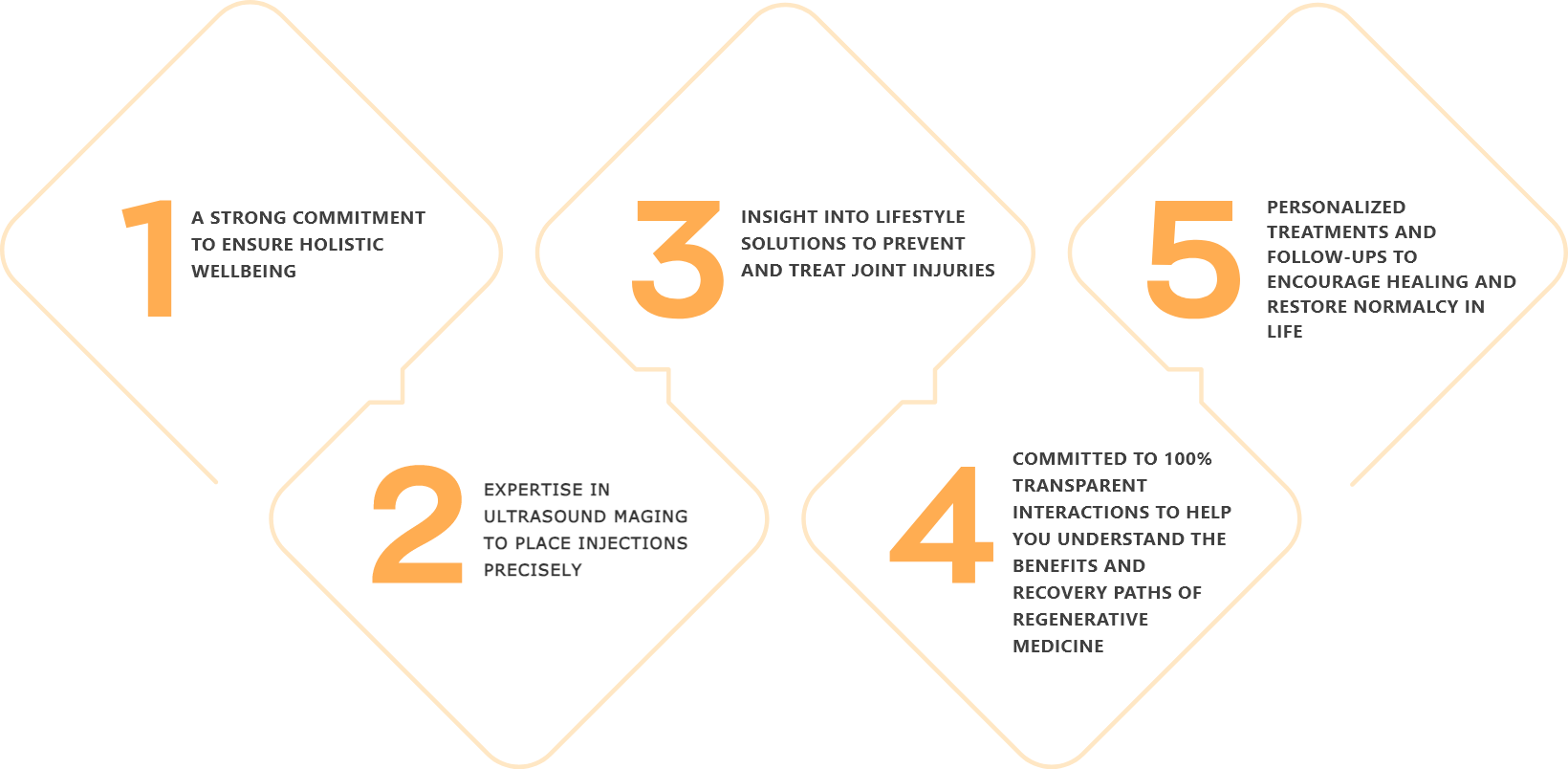
StemX is California's leading provider of holistic and regenerative medicine services. Our experts don't just offer popular treatments, but customized medical solutions based on individual needs.
Located in Solana Beach, California, the StemX clinic is composed of a team of expert doctors with years of experience administering regenerative medicine treatments for joint disease. Our team has:





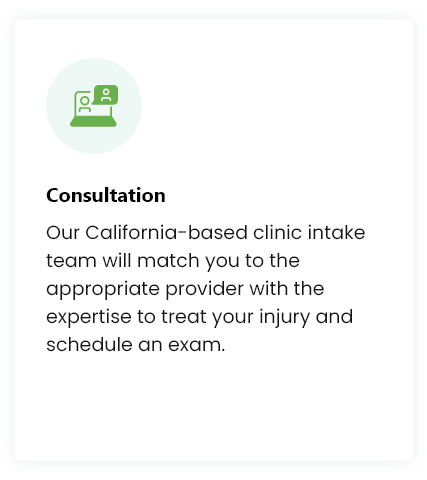
How To Get Started
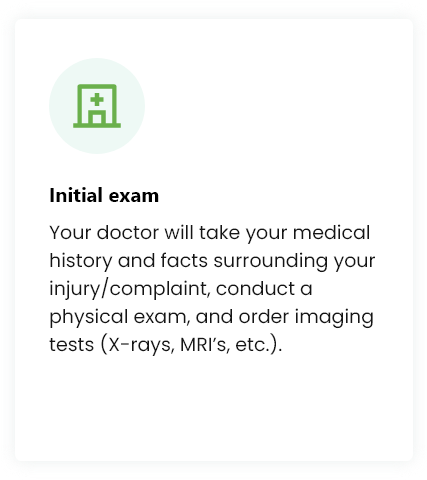
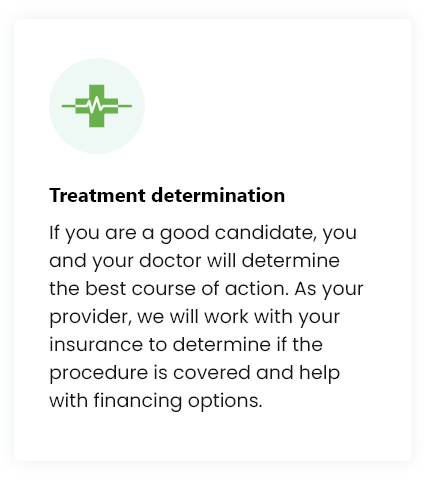
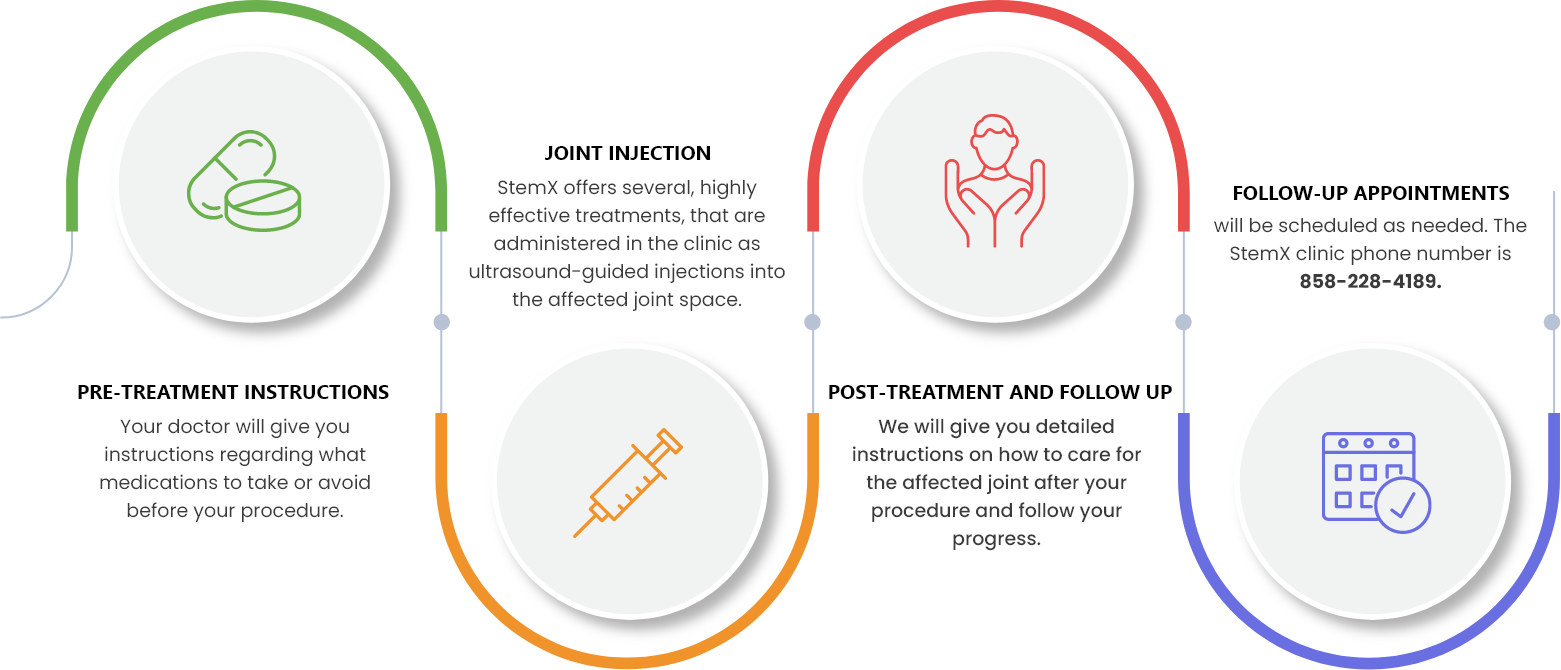
Treatment Procedure
While each treatment may be customized, you can expect your experience to be similar to the following:




All procedures are conducted in our Solana Beach, California clinic. 124 Lomas Santa Fe Dr #206, Solana Beach, CA 92075.
Frequently Asked Questions
Some meniscus tears are stable tears or located on a vascularized portion of the cartilage. These tears have the best chance of healing especially with regenerative medicine therapy. More serious tears will not heal on their own.
A torn meniscus can take from 4-8 weeks to heal depending on the location and severity of the tear. Regenerative medicine and strength building exercises and accelerate healing time significantly.
An untreated meniscus tear can become larger and get wedged into the joint. This can cause significant pain and loss of function or lead to osteoarthritis of the knee and require surgery to repair.
Pain from a torn meniscus usually presents on the inner (medial) or lateral (outer) side of the knee. An effective torn meniscus treatment, like Wharton’s Jelly or amniotic fluid allografts, can reduce this pain by stimulating healing.
PRP can work as a torn meniscus treatment. More effective treatments for torn meniscus are Wharton’s Jelly and amniotic fluid injections containing high levels of growth factors that promote healing in areas with poor blood circulation..
A steroid injection is not an ideal treatment for a torn meniscus. They do help alleviate pain but have significant side effects and cannot be used very often.
Most data shows that PRP injections last up to 9 months but this can vary by person and with injury severity. More effective regenerative medicine treatments (Wharton’s Jelly, amniotic fluid allografts) may last significantly longer.
If the meniscus is missing stem cells cannot regrow it. However, treatments that promote stem cell growth and proliferation can help to heal meniscus tears.



