What is a rotator cuff tear?
Rotator cuff tears are usually partial tears in the muscles or tendons that support the shoulder joint where the humerus fits into its socket in the shoulder blade (the glenohumeral joint).
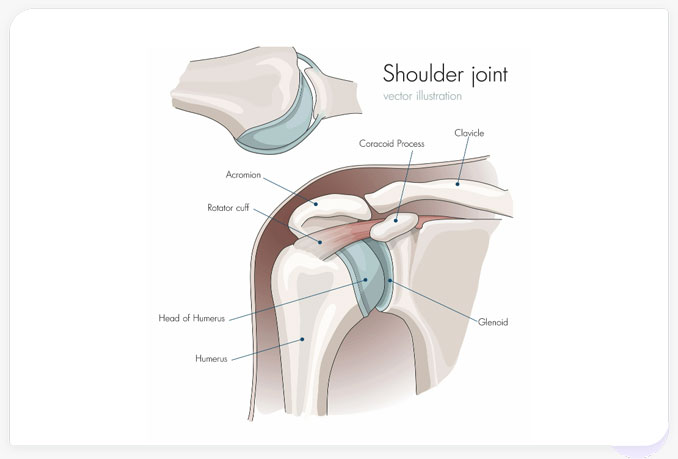
The arm's position in the shoulder socket is maintained by the rotator cuff which is a group of four muscles connected to the head of the humerus by tendons. The rotator cuff allows the arm to be raised and rotated (see Figure 1).
When a tendon in the rotator cuff tears (usually the supraspinatus tendon), it peels away from the head of the humerus. Full thickness tears involve the complete detachment of the tendon from the shoulder and require surgery to fix, whereas partial tears can usually be treated non-surgically with regenerative medicine and other supportive therapies.
Rotator cuff tears and rotator cuff tendonitis are very common injuries with up to 3 million people reporting injury every year.
Figure 1. The shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) is a ball and socket joint between the scapula (shoulder blade) and the humerus (upper arm bone between the shoulder and elbow). The glenoid is the portion of the scapula that forms the shoulder joint with the humerus. The rotator cuff acts to stabilize the shoulder and allow for its extensive range of motion. Shown is a partial tear of the rotator cuff.
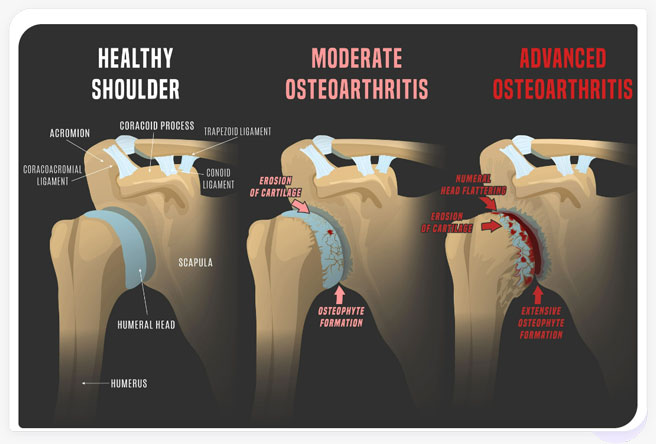
The rotator cuff lies the acromion bursa which protects the muscles and tendons from rubbing against the underlying bones. Damage to the rotator cuff can cause bursitis or inflammation of the bursa. This in turn can place more stress on the shoulder joint and can lead to osteoarthritis if the cartilage becomes damaged (see Figure 2).
Figure 2. Osteoarthritis (OA) of the shoulder joint. Damage to joint tissue including rotator cuff tears can lead to the development of osteoarthritis because of joint instability. As OA progresses, the articular cartilage erodes and osteophyte formation increases. Degeneration of the joint causes significant pain, stiffness, and loss of function.
Causes, Signs & Symptoms of Rotator Cuff Tears

A dull deep ache in the shoulder is a common rotator cuff tear symptom.
Other torn rotator cuff tear symptoms include:- Shoulder pain. Tears caused by trauma may cause intense shoulder pain and arm weakness. With degenerative tears, mild pain may worsen over time and at night, painful especially when doing overhead activities.
- Crepitus. Feeling or hearing a crunching or popping sound when rotating the shoulder.
- Weakness. Loss of shoulder strength and difficulty lifting objects.
Causes And Risk Factors for Rotator Cuff Tears
As with many joint injuries, the biggest cause or risk factor for rotator cuff tears or rotator cuff pain is repetitive use and wear and tear leading to degeneration of the tendons.
Others causes and risk factors include:- Repetitive overhead activities. Throwing, swimming, swinging a racket etc.
- Extended periods of heaving lifting.
- Acute trauma.
- Falls and other accidents. Broken collar bones or dislocated shoulder can damage the rotator cuff.
- Bone spurs. Rubbing of bone spurs against the tendon can cause it to fray or tear.
- Age. In addition to wear and tear over time, decrease blood flow to the rotator cuff can be detrimental to tendon health.
- Poor posture.
- Smoking.


Rotator cuff tears are diagnosed by our Specialists using a multipronged approach.
- Medical History: Our doctors will ask you about the nature of your shoulder pain (e.g., when and under what conditions you experience shoulder pain). They will ask about prior surgeries, accidents, and trauma to the shoulder.
- Physical Exam: The doctor will examine the shoulder and may perform a rotator cuff injury test (e.g., Drop Arm Sign, Lateral Jobe Test, Lift Off Test) to isolate the rotator cuff pain location.
- Imaging with X-Rays, MRI, or ultrasound: X-rays are used to check for shoulder pain due to osteoarthritis or bone spurs. A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan may be used to determine if a tendon in the rotator cuff is torn.
Treatment Options
The StemX clinic offers a range of customized Regenerative Medicine solutions for rotator cuff tears.
The StemX Approach
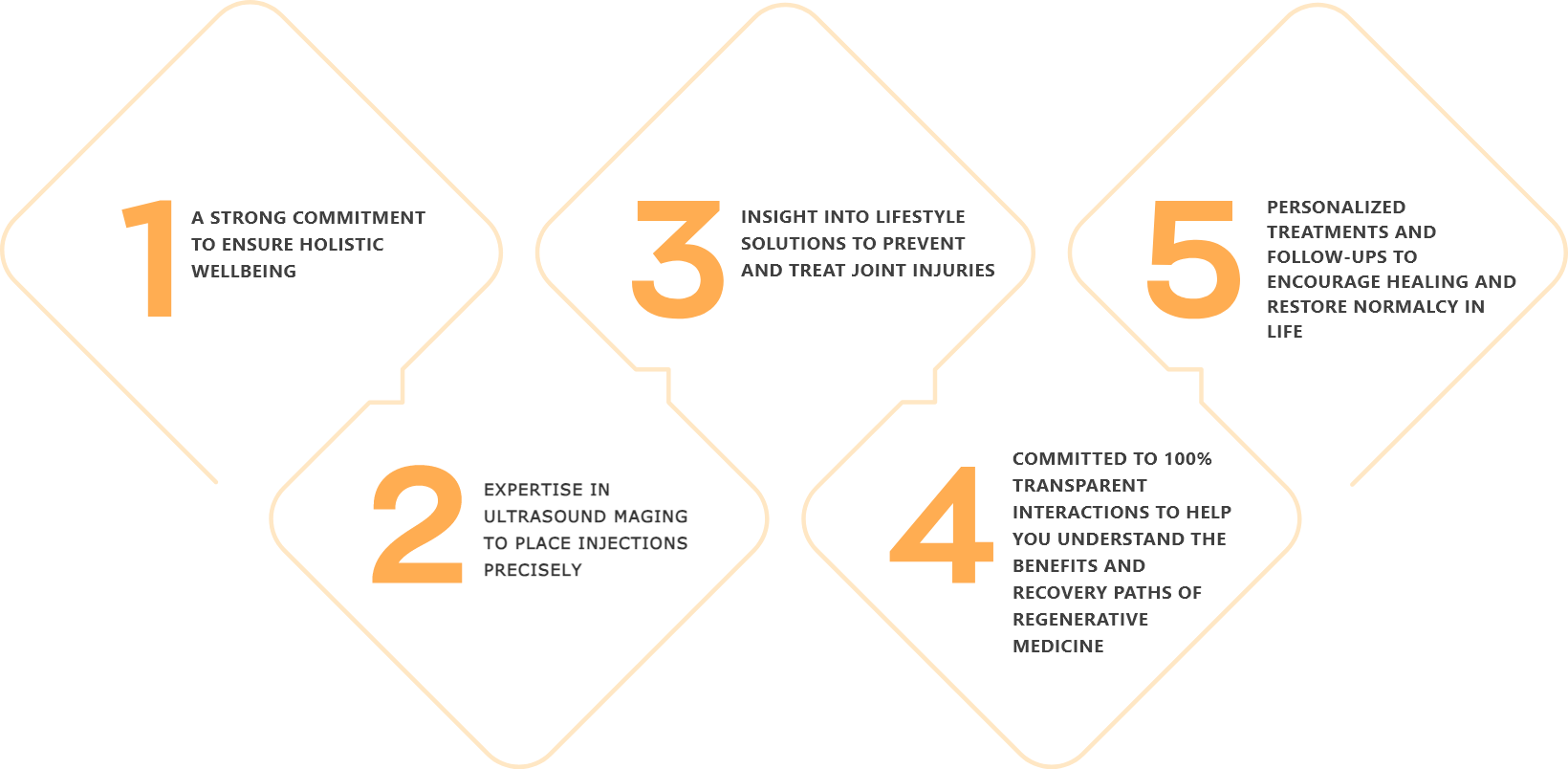
StemX is California's leading provider of holistic and regenerative medicine services. Our experts don't just offer popular treatments, but customized medical solutions based on individual needs.
Located in Solana Beach, California, the StemX clinic is composed of a team of expert doctors with years of experience administering regenerative medicine treatments for joint disease. Our team has:





How To Get Started
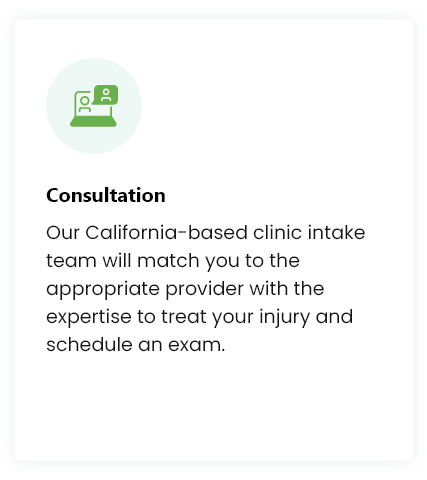
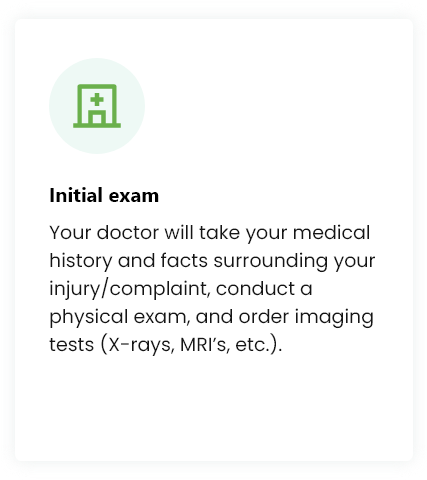
Treatment Procedure
While each treatment may be customized, you can expect your experience to be similar to the following:
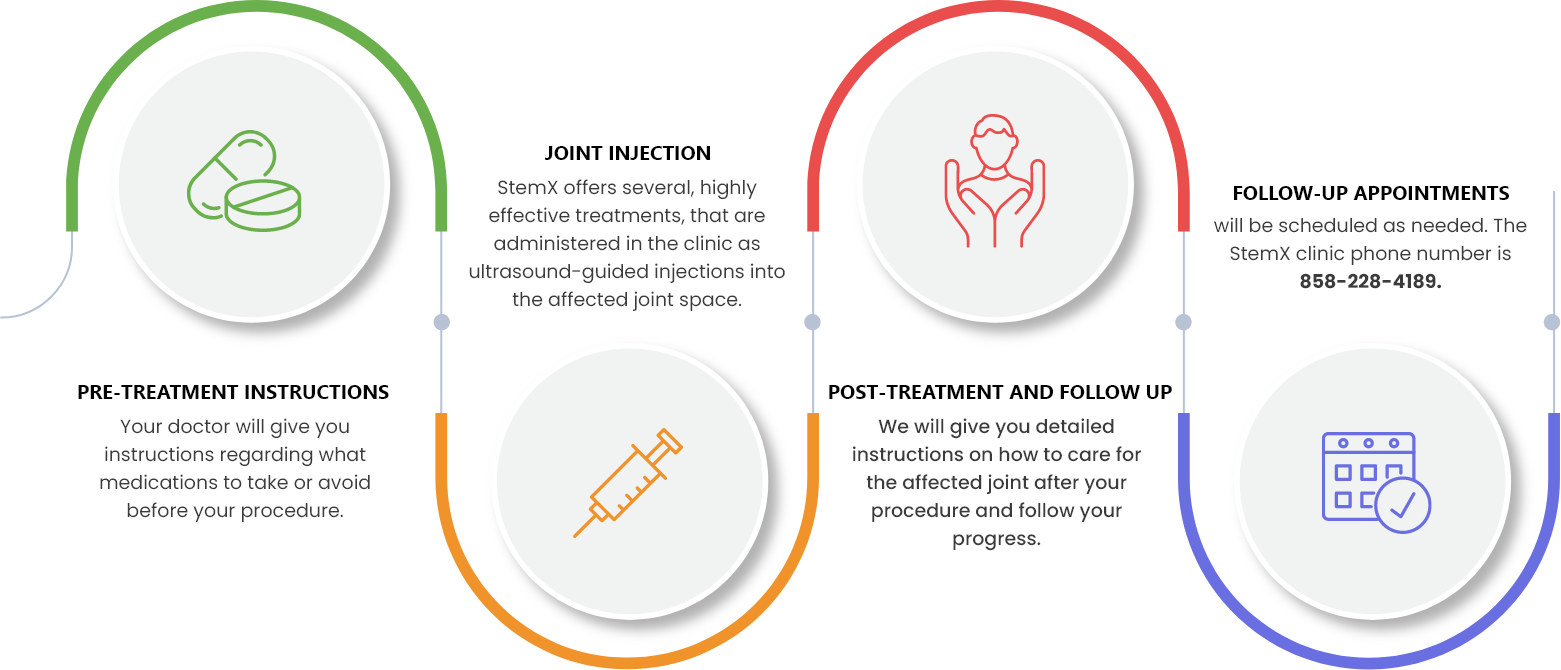




All procedures are conducted in our Solana Beach, California clinic. 124 Lomas Santa Fe Dr #206, Solana Beach, CA 92075.
Frequently Asked Questions
Surgery is not necessarily needed for all rotator cuff tears. Partial tears and sprains can heal with rest, physical therapy, and regenerative medicine. Steroids are also used for pain but have side effects that can affect tendon health.
Mild or partial rotator cuff tears can heal with proper care in ~4 weeks. Moderate tears may take 4-6 months. Full tears require surgery.
Partial tears may be asymptomatic or cause deep shoulder pain on the end of the shoulder. Weakness, inability to lift items, and pain when lifting the arm are common symptoms.
Not necessarily. Partial tears can be treated without surgery. Full thickness tears will make it very difficult to move the arm and will be very painful without surgical intervention.
Untreated partial tears can get worse if left untreated especially if the tendons experience continues physical stress.
Regenerative medicine can speed the healing of partial tears. Physical therapy is almost always recommended as well to rebuild strength in the tendons.
Untreated partial tears can get worse if left untreated especially if the tendons experience continues physical stress. Pain can gradually worsen, and function of the arm can decrease.
Physical therapy for a rotator cuff tear when done correctly should improve function of the shoulder and is typically recommended.
Some rotator cuff tears are asymptomatic. If the tear is very minor or just sprained, it is possible it will heal on its own if not further injured. This may be difficult to ensure, however.
A full thickness tear will require surgery to fix and be quite painful but is not a life-threatening emergency.
Rest, physical therapy, and regenerative medicine treatments prevent worsening of tears and promote healing.
Regenerative medicine treatments can last from months to years depending on the patient's activity levels and disease severity. Athletes may need repeated treatments, for example.
Regenerative medicine treatments cause minimal discomfort and consist of a simple injection into the joint space. The joint may be sore a few days after the injection.



